What are the Stages of Gum Disease?
Gum disease is described as swelling, tenderness or infection in the tissues of the gum. It is caused by the build up of plaque, as the bacteria in the plaque reacts with the left over tiny food particles that forms acid. This acid can cause many gum problems leading to tooth sensitivity or tooth decay.
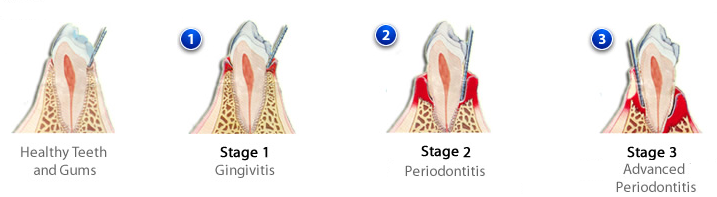
Stages of gum disease
Gingivitis (stage 1)
Early stage of gum disease is called gingivitis, an inflammation and soreness of gums. The main reason is the plaque that irritates gum tissues.
- Signs and symptoms
- Swelling in gums
- Tenderness in gums
- Bleeding from the gums especially when brushing and flossing
- Changes in the color of the gum
- Bad or unpleasant breath
-
- Treatment for gingivitis
Visiting the dentist regularly will help you know if you have any gum disease. As gum diseases are mainly caused by the build up of plaque, it becomes hard over a time, which is called tartar and it can only be cleaned by a dentist. If there is a severe condition, you may require other dental treatments. Treatment at an early stage is simple, but leaving the problem untreated will lead to more complex treatments.
Periodontitis (stage 2)
If gingivitis is not treated in the initial stages, it will start damaging the tissues of the gum as well as the bone that supports and holds the teeth. As the advance disease damages the gum tissues, your teeth becomes loose. If not treated, your teeth may fall.
- Signs and symptoms
- Color of the gums becomes red-purple or bright red
- Loose teeth
- Swelling and bleeding gums
-
- Treatment
In most of the cases scaling is done to clean the hardened plaque which is called tartar. Periodontal disease some times require root canal treatment. In a root canal treatment, the nerve that is infected and causing problem is removed and restored with the dental crown.
Advanced Periodontitis (stage 3)
In an advanced stage of periodontal disease, the bone that holds the teeth gets totally damaged and leads to loosening or shifting of your teeth. Many times gum disease in this stage can’t be treated, you may need to get your teeth removed.
- Signs and symptoms
- As the bone that supports the teeth gets damaged, teeth becomes loose.
- Pus from gums
- Receding gums, a situation where gums are pulled away from the teeth
- Space appearing in between the teeth
-
- Treatment
Treatment of periodontitis at an advanced stage depends on how severe your gum tissues are damaged. Options for treating advanced periodontal disease can be surgical or non surgical. Non surgical treatment scaling or root canal treatment. Scaling removes the hardened plaque and root canal treatment removes the infected nerve.
In later stages where non surgical treatment cannot help with this disease, surgical procedures may be required which includes gingivectomy, a procedure of removing gum tissues that are overgrown thus leveling the gum to its original position. A flap surgery, a procedure where access is made to the gum pockets that are infected by separating gums gently from the teeth.
You may also like to read:
What Causes Gum Problems?